Understanding Program Derived Addresses (PDAs) in Solana development
Sandeep Donepudi / March 27, 2023 (1y ago)
3 min read • ––– views
Ever wondered what Program Derived Addresses (PDAs) are in Solana development and why they matter? In this post, we’ll explore PDAs, their importance, and some practical use cases. Let’s dive in! 🚀
What are PDAs?
PDAs are special accounts on the Solana blockchain that do not have a private key. They are created using a parent program ID, a seed array, and a bump seed. The bump seed ensures that the PDA does not lie on the ED25519 elliptic curve, meaning it is secure and does not expose a private key.
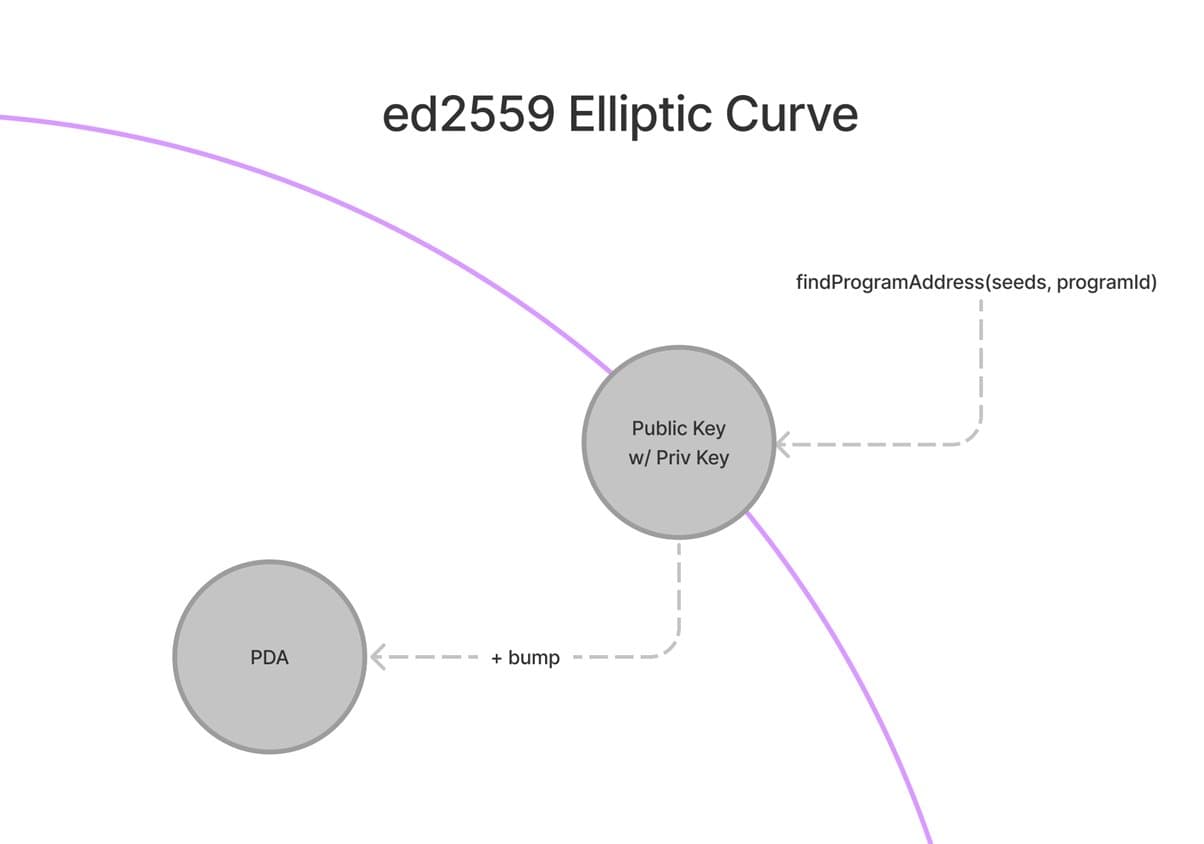
Why are PDAs Important?
PDAs offer several key benefits:
- Secure State Storage: They allow programs to store state variables without exposing a private key.
- Efficient Data Structures: PDAs can create hashmap-like structures for easy data updates.
- Cross-Program Invocations (CPI): They facilitate better code composability by enabling different programs to interact seamlessly.
Solving Trust Issues in DeFi
PDAs help address trust issues in decentralized finance (DeFi) accounts and enable secure communication between different programs on the Solana blockchain. This is crucial for creating fast and efficient decentralized applications (dApps).
Use Case: Profile Picture (PFP) Program
Imagine a Solana program that allows users to set an NFT as their default profile picture. This program consists of two parts:
- PFP Program: Responsible for creating accounts and storing the profile picture.
- Core Program: Acts as a proxy for user inputs.
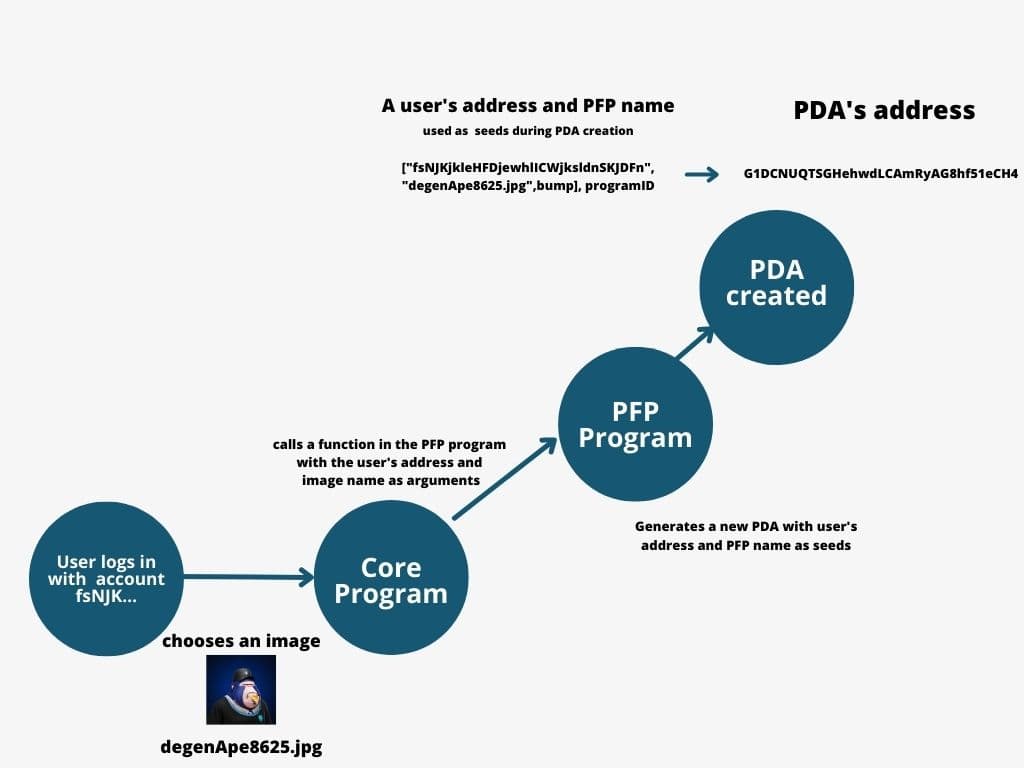
Secure Storage with PDAs
Instead of storing the private key on-chain, the PFP program can use a PDA to securely store the user's chosen NFT. This way, the program can update the user's profile picture without exposing the private key to potential hacks.
Efficient Data Management
PDAs can also create hashmap-like structures, allowing developers to efficiently store and retrieve data related to specific users. For instance, a PDA's seeds can map a user's public key to their chosen NFT avatar.
Cross-Program Invocations (CPI)
CPI is the process of one program calling a function in another program. This is crucial in the Solana ecosystem as it allows for better code composability, reusability, and collaboration among different programs.
PDAs and CPIs Working Together
PDAs enable secure communication between programs during CPIs by storing state variables and allowing parent programs to modify data on their behalf. This ensures trustless and secure transactions.
Changing Profile Pictures
When a user wants to change their profile picture, the core program initiates a CPI by calling a function in the PFP program (e.g., changePFP()). The PFP program then verifies the PDA's parent before allowing the update to proceed.
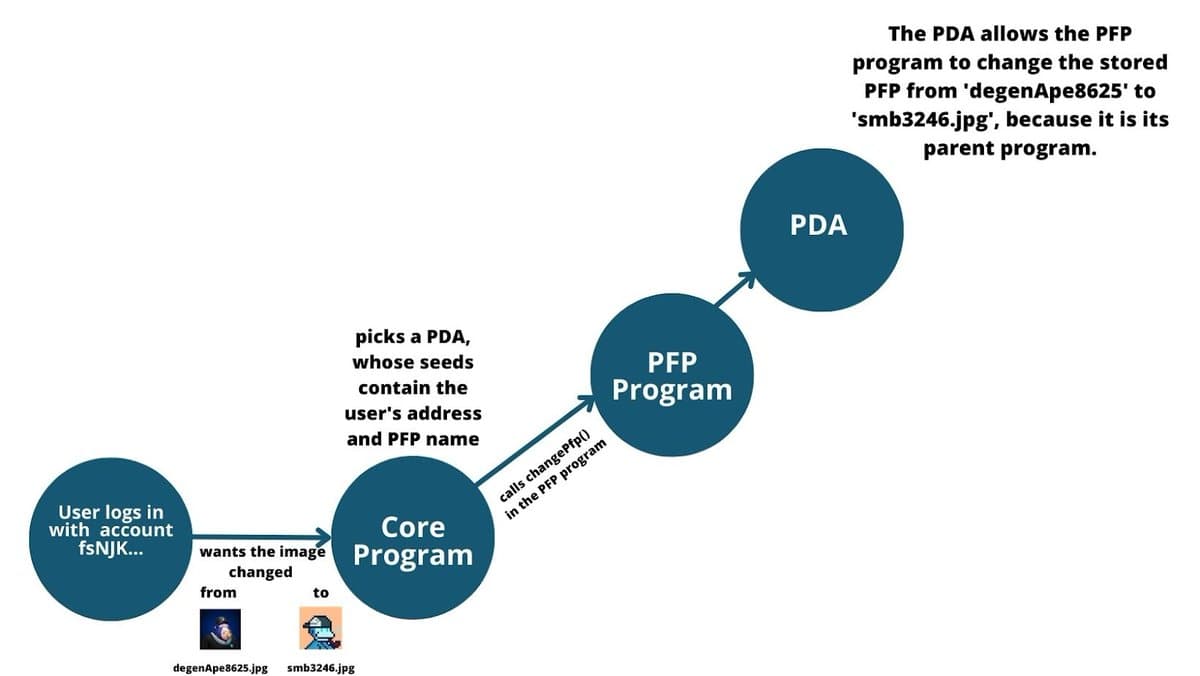
Conclusion
In conclusion, PDAs and CPIs are essential components of Solana programming that enable fast and secure dApp development. By understanding and utilizing PDAs, developers can build secure and trustless services on the Solana blockchain. Happy building! 🚀